After a seven-year development process, NASA and its partners are excited to send the James Webb Space Telescope into space on July 6. The telescope is currently on a one-month journey to reach its observing perch beyond the moon. It still has one major milestone to achieve, which is reaching its L2 orbit – a million miles away – where it will observe the earliest stars and distant worlds. The next step for the JWST is to reach its yearly orbit.
During this time, the Webb mission team will begin testing its four scientific instruments in orbit. These instruments will record infrared wavelengths from galaxies and stars that were formed around a billion million years ago. They will also be used to align the telescope’s primary mirror segments. The five mirror segments will act as one light-collecting surface. The mission is expected to begin in late June or early July 2022.
The James Webb Space Telescope will launch on Dec. 25, 2021. It should have enough fuel to last for its entire mission. It will also work in tandem with the Hubble Space Telescope, which is currently in good health and is likely to be used by the new telescope in its early years. It will also follow real-time observations from ground-based space telescopes. It will have the potential to help discover many exoplanets.
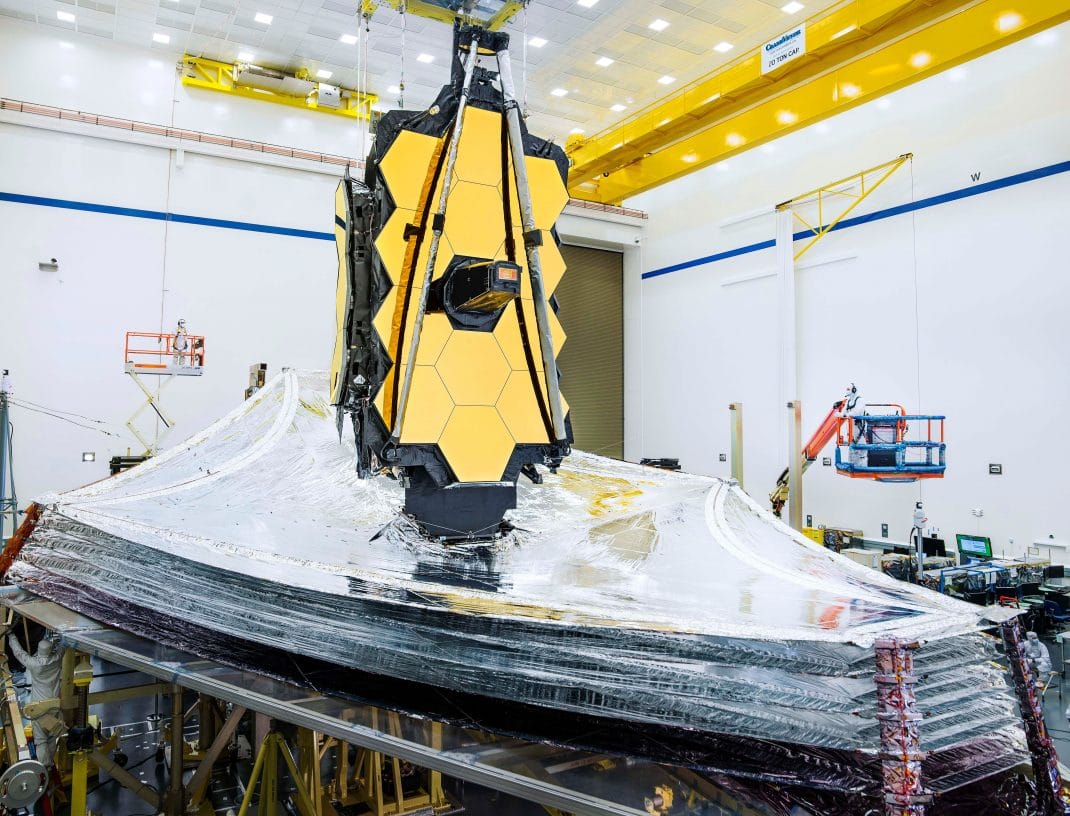

In addition to detecting planets, the telescope will also help astronomers better understand dark energy, which is the force that pushes the universe into expansion. In addition to the mass of the stars, dark energy is one of the most mysterious forces in the universe. Researchers are uncertain how fast the universe is expanding. By examining this phenomenon with a new space telescope, scientists will be able to answer the big question: “How old is the universe?”
The new telescope will be a natural successor to the Hubble, which launched in 1990. The project was originally scheduled to launch in 2007 but a major redesign postponed the launch date to 2022. Nevertheless, construction of the observatory was completed by the end of the year 2016, and testing work began in January 2018. Its launch date was delayed due to the Covid-19 pandemic. So far, Webb is an important step towards the exploration of the universe.
The mission will include testing four scientific instruments in orbit to see if they are in good working order. These instruments will allow the telescope to detect and record infrared wavelengths from ancient stars and galaxies. The Webb will launch on December 24, 2021, from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana. It is estimated that the telescope will last for seven years, allowing astronomers to discover life in the universe.
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is an international collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian National Astronautics and Space Administration (Nasa). The telescope is named after the late astronaut and NASA administrator James E. “Jim” W. Webb, who played a major role in the Apollo program. The telescope was launched to space in July 2013 and has already received numerous accolades. During its construction, a total of eight countries contributed approximately $2 billion for the mission.
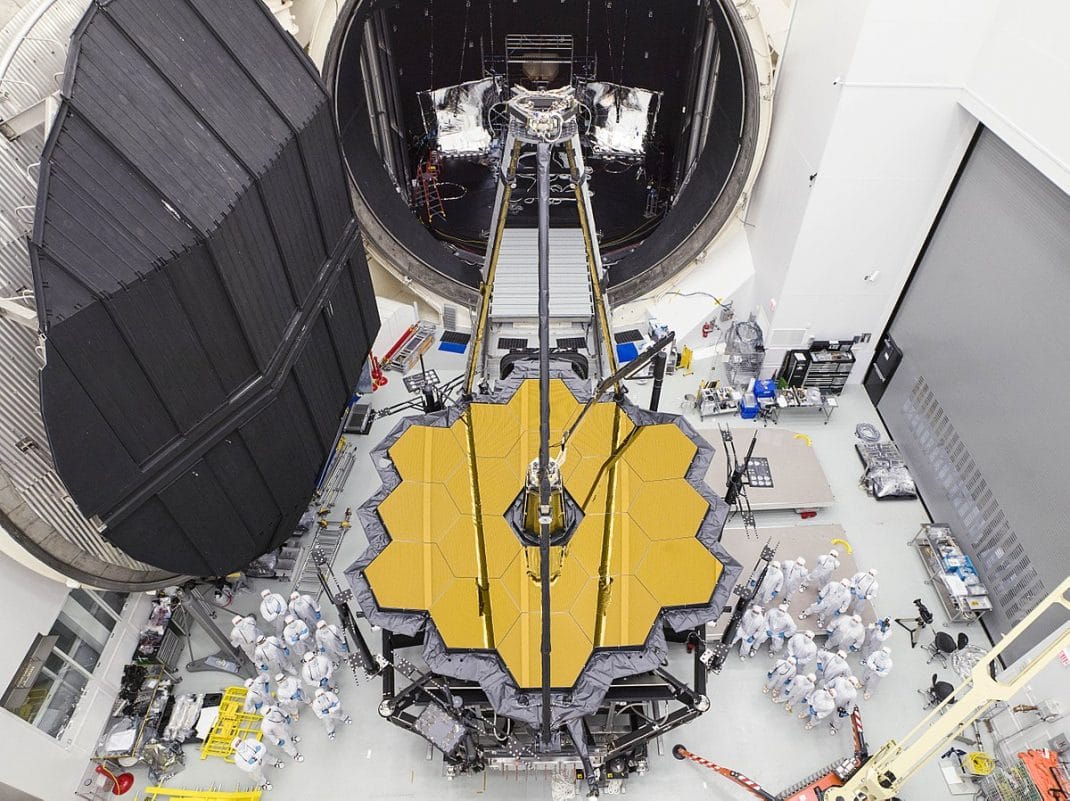

The James Webb Space Telescope will cost $10 billion and will be launched on a European Ariane 5 rocket in December 2021. Its mission is to study the early universe and detect faint infrared light from the earliest stars and galaxies. The telescope will also be capable of detecting the first stars. It will help astronomers study the origin of life and the origin of the universe.
After it has completed the launch, the telescope will begin its tests. It will be pointing at a bright star to demonstrate target acquisition and locking. The telescope will also begin its first science mission, as it will start measuring the distance of stars and galaxies. It will then move on to routine science missions. In a few months, the telescope will be able to begin observing the universe at a quarter billion years ago.