XRP is a digital asset that was created by Ripple Labs, Inc. in 2012. It is a cryptocurrency that was designed to facilitate cross-border payments and provide liquidity for financial institutions. In this article, we will discuss the history of XRP, its purpose, technology, regulatory challenges, future, and potential.
Contents
History of XRP
In 2004, Ryan Fugger created RipplePay, a decentralized payment system that allowed users to send and receive money in any currency. Jed McCaleb, Chris Larsen, and Arthur Britto acquired RipplePay in 2012 and created Ripple Labs, Inc. They then developed the Ripple protocol, which was designed to enable banks and other financial institutions to conduct cross-border payments faster and more efficiently.
– Cardano (ADA): A Third-Generation Cryptocurrency
The first version of the Ripple protocol was released in 2012, and it used XRP as its native digital asset. XRP was created to serve as a bridge currency that could facilitate cross-border payments between different currencies. It was also designed to provide liquidity to financial institutions by allowing them to use XRP as a source of funding.
Purpose of XRP
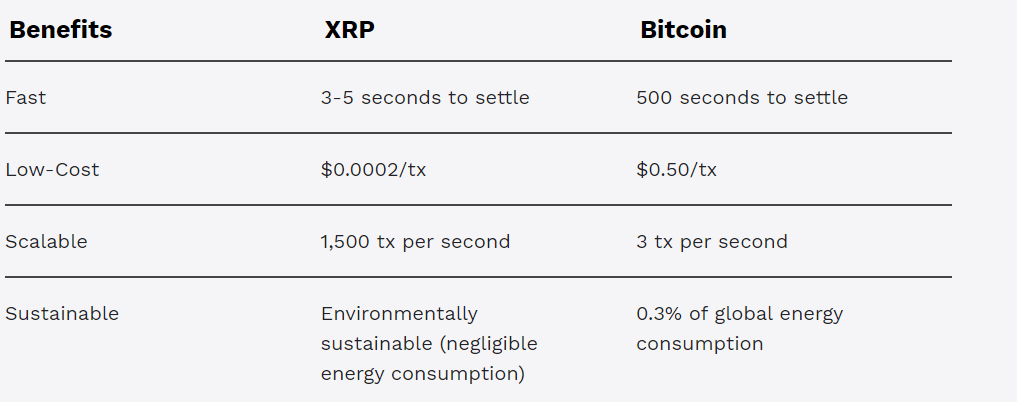
The purpose of XRP is to provide a fast, efficient, and cost-effective way for financial institutions to conduct cross-border payments. It is designed to provide liquidity to financial institutions by allowing them to use XRP as a source of funding. XRP is also used as a bridge currency that can facilitate cross-border payments between different currencies.
Technology Behind XRP
XRP is built on a distributed ledger technology called the XRP Ledger. The XRP Ledger is a decentralized, open-source blockchain that allows for fast and secure transactions. It uses a consensus algorithm called the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA), which is designed to enable fast and efficient transaction processing.
Unlike other cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, XRP is not mined. All 100 billion XRP tokens were created at the inception of the network. Ripple Labs owns a majority of the XRP tokens, but the company has promised to lock up a significant portion of the tokens in escrow to provide stability to the network.
Regulatory Challenges
XRP has faced several regulatory challenges in the past few years. In December 2020, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filed a lawsuit against Ripple Labs, alleging that XRP was an unregistered security. The SEC argued that Ripple Labs had conducted an unregistered securities offering by selling XRP to investors.
The lawsuit caused several exchanges to delist XRP, and the price of XRP plummeted. Ripple Labs has denied the allegations and has vowed to fight the lawsuit. The case is still ongoing, and the outcome is uncertain.
– Polygon (MATIC): A Comprehensive Guide to the Layer-2 Scaling Solution
Future and Potential
Despite the regulatory challenges, XRP has several potential use cases. Its ability to facilitate fast and efficient cross-border payments makes it an attractive asset for financial institutions. It can also be used as a bridge currency to facilitate trade between different currencies.
Several financial institutions have already partnered with Ripple Labs to use XRP in their cross-border payment systems. These institutions include Santander, Standard Chartered, and American Express.

Conclusion
XRP is a digital asset that was created to facilitate cross-border payments and provide liquidity for financial institutions. It was designed to provide a fast, efficient, and cost-effective way for financial institutions to conduct cross-border payments. XRP is built on the XRP Ledger, a decentralized blockchain that uses the RPCA consensus algorithm. Despite the regulatory challenges, XRP has several potential use cases, and its ability to facilitate fast and efficient cross-border payments makes it an attractive asset